
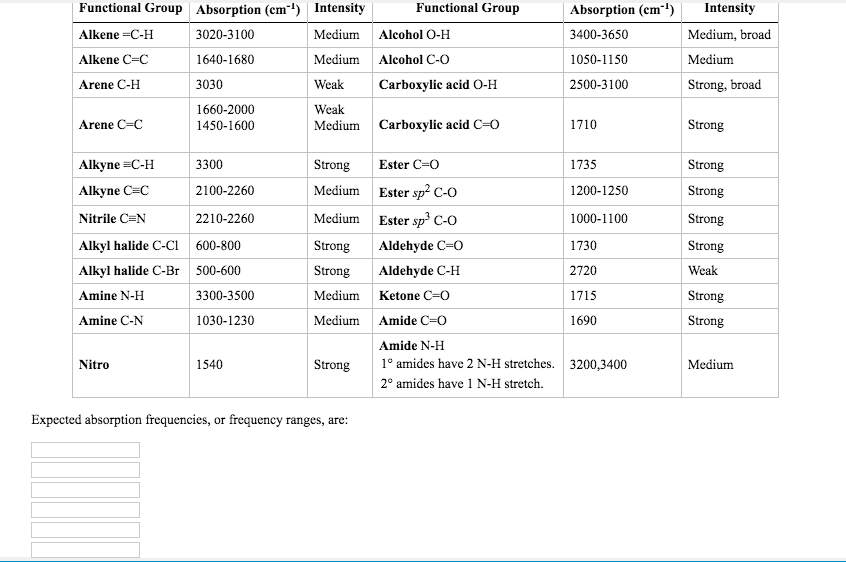
According to this, the spectral radiance of a body for frequency ν at absolute temperature T is given byī ν ( ν, T ) = 2 h ν 3 c 2 1 exp ( h ν k B T ) − 1 . If you were to look up - on a 'table of characteristics of IR absorption' - you would see that a signal appearing at approximately 2100-2260 cm-1 depicts a. The information in Table 6.1 can be summarized in the diagram for easier identification (Figure 6.3b), in which the IR spectrum is divided into several regions, with the characteristic band of certain groups labelled. The relationship given by Planck's radiation law, given below, shows that with increasing temperature, the total radiated energy of a body increases and the peak of the emitted spectrum shifts to shorter wavelengths. While Planck originally regarded the hypothesis of dividing energy into increments as a mathematical artifice, introduced merely to get the correct answer, other physicists including Albert Einstein built on his work, and Planck's insight is now recognized to be of fundamental importance to quantum theory.Įvery physical body spontaneously and continuously emits electromagnetic radiation and the spectral radiance of a body, B ν, describes the spectral emissive power per unit area, per unit solid angle, per unit frequency for particular radiation frequencies.
Table 2 depicts the complete results of antibiotic resistance patterns and compares the ESBL-negative and ESBL-positive isolates. Some tables of data fine it down, so that they will tell you that an absorption from 1230 - 1250 is the C-O bond in an ethanoate. The portion of the infrared region most useful for analysis of organic compounds is not immediately adjacent to the visible spectrum, but is that having a. In 1900, German physicist Max Planck heuristically derived a formula for the observed spectrum by assuming that a hypothetical electrically charged oscillator in a cavity that contained black-body radiation could only change its energy in a minimal increment, E, that was proportional to the frequency of its associated electromagnetic wave. Characterization of Hypervirulent Extended-Spectrum -Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Among Urinary Tract Infections. LCD display, go button and Sample Table functionality. Īt the end of the 19th century, physicists were unable to explain why the observed spectrum of black-body radiation, which by then had been accurately measured, diverged significantly at higher frequencies from that predicted by existing theories. External input and output beam options for custom experiments. In physics, Planck's law describes the spectral density of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature T, when there is no net flow of matter or energy between the body and its environment. FTIR spectrum information and bond relationship. The classical (black) curve diverges from observed intensity at high frequencies (short wavelengths). FTIR spectrum, please contact me at or for any mistakes or discussion. Note: strong, medium, weak refers to the length of the peak (in the y axis direction). Shown here are a family of curves for different temperatures. Planck's law accurately describes black-body radiation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
